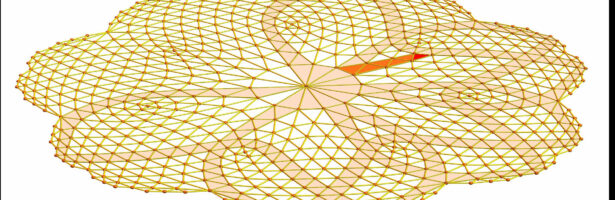
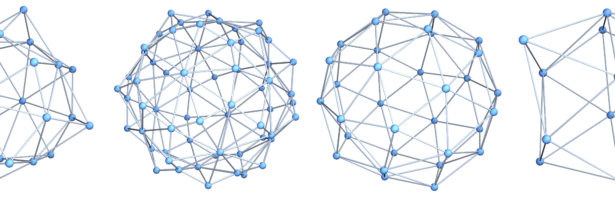
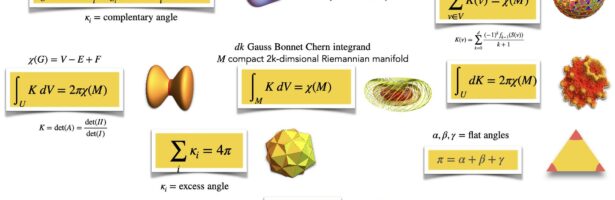
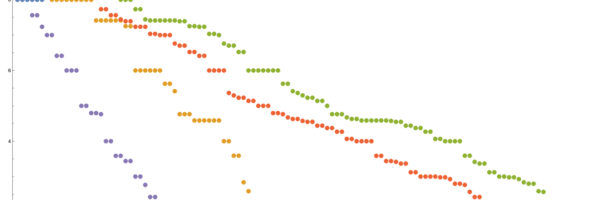
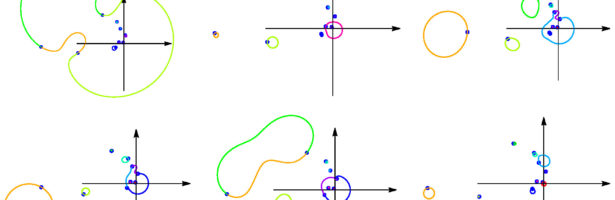
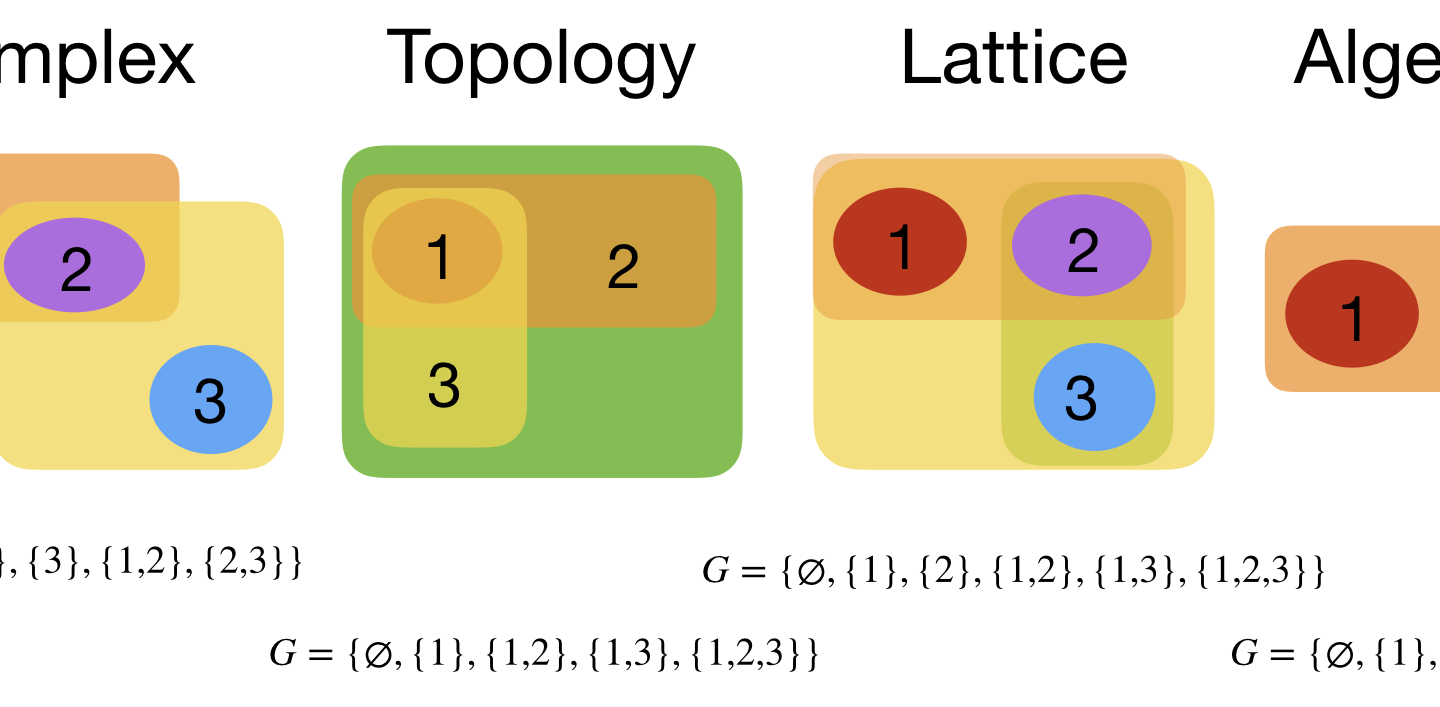
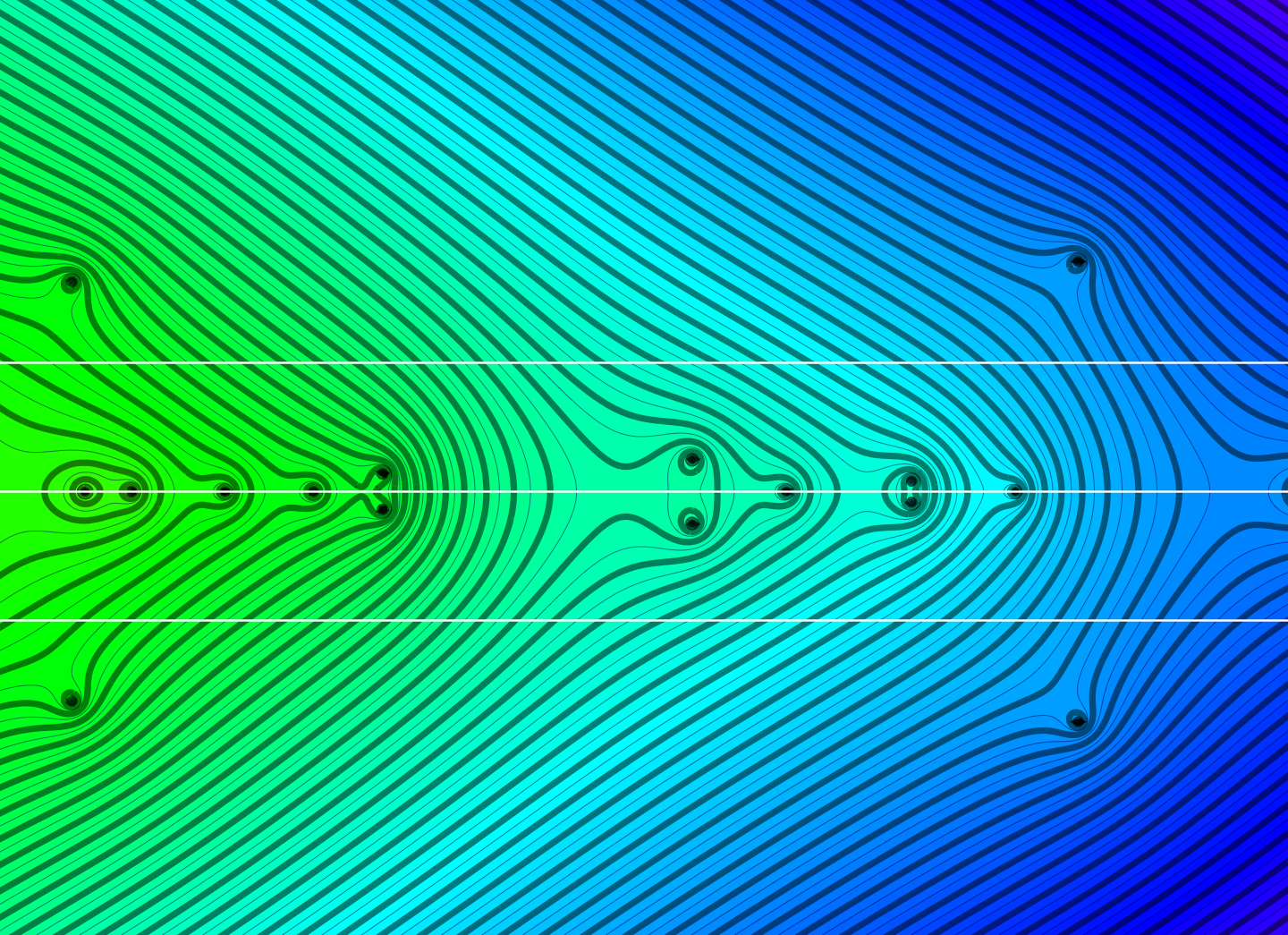
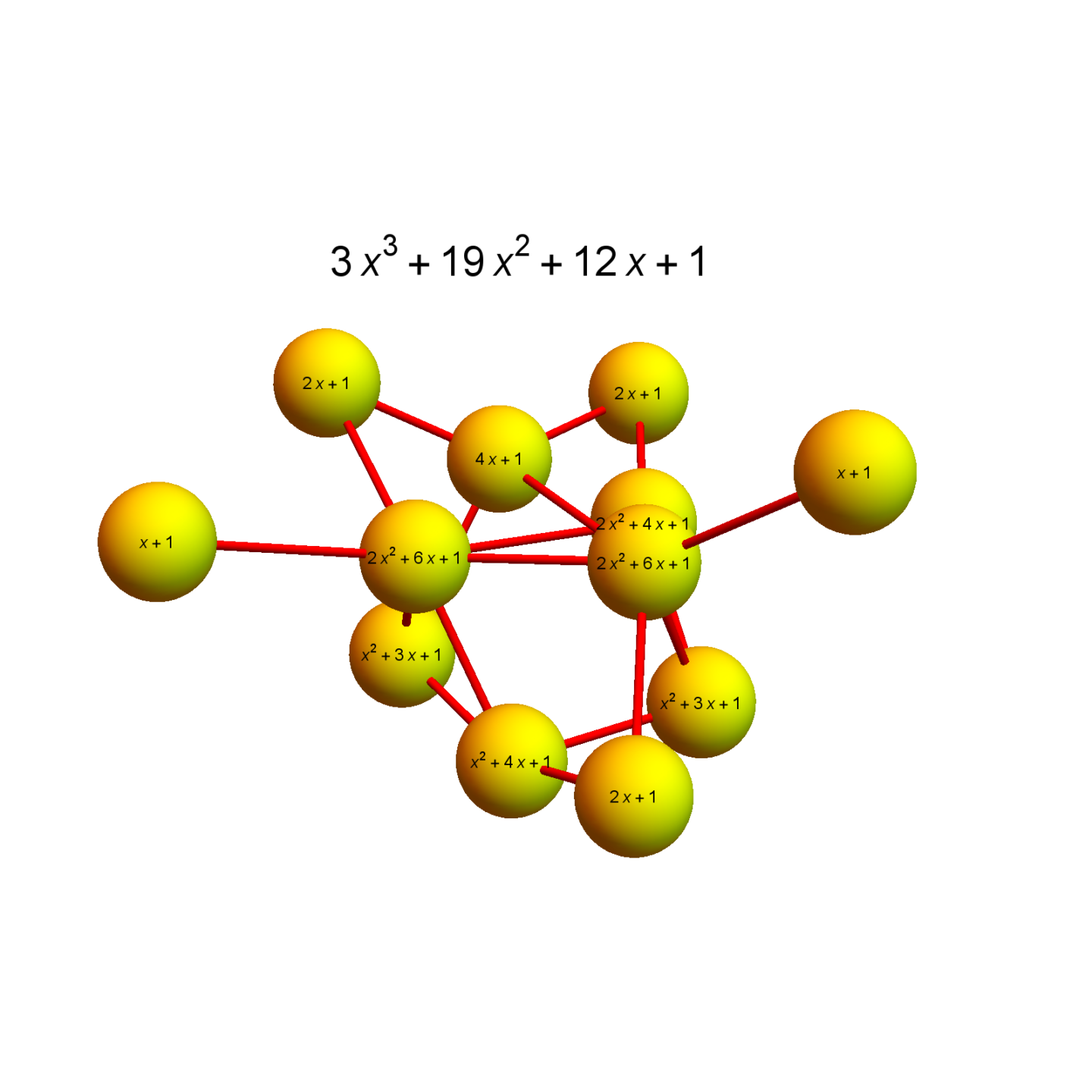
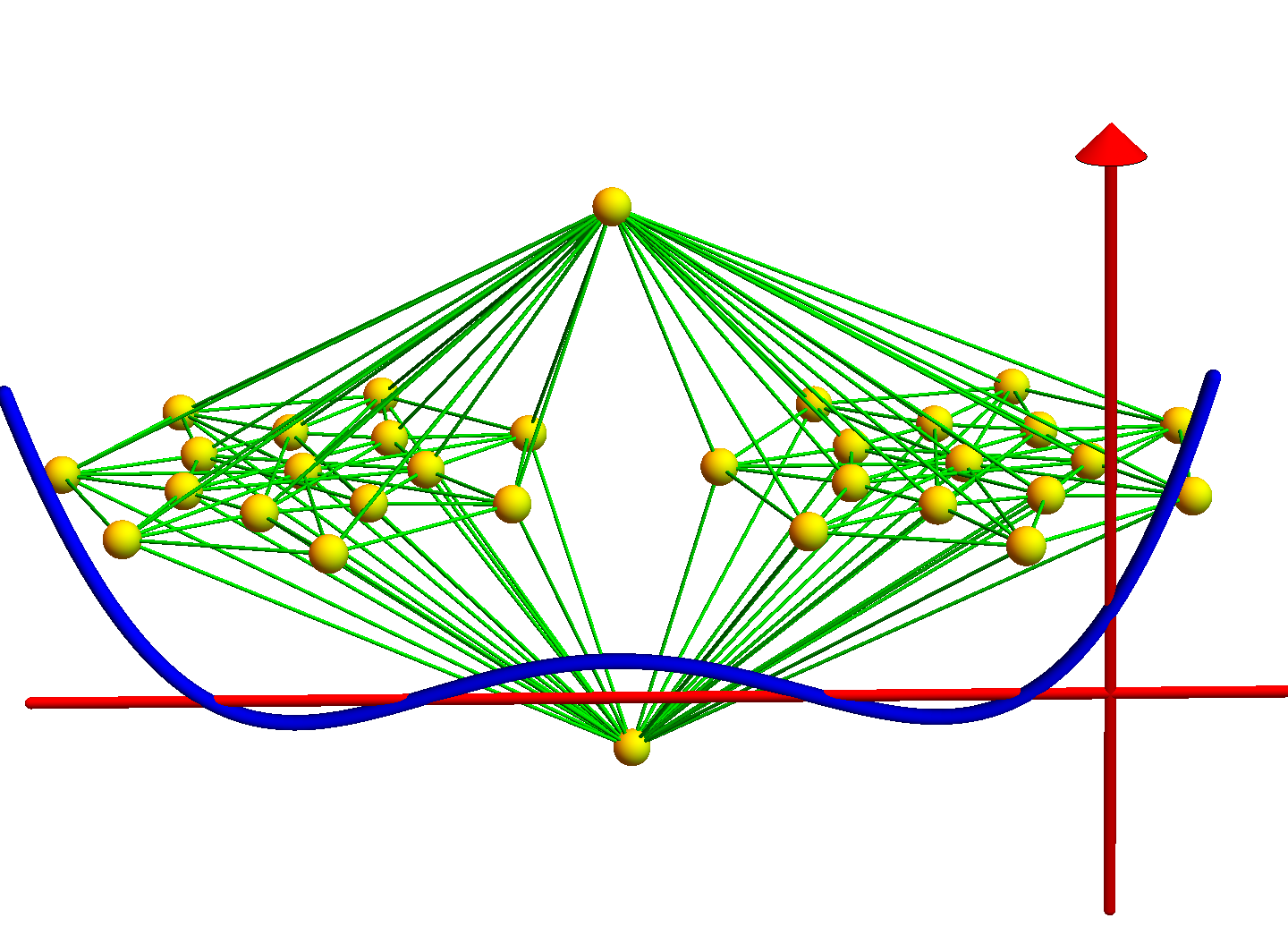
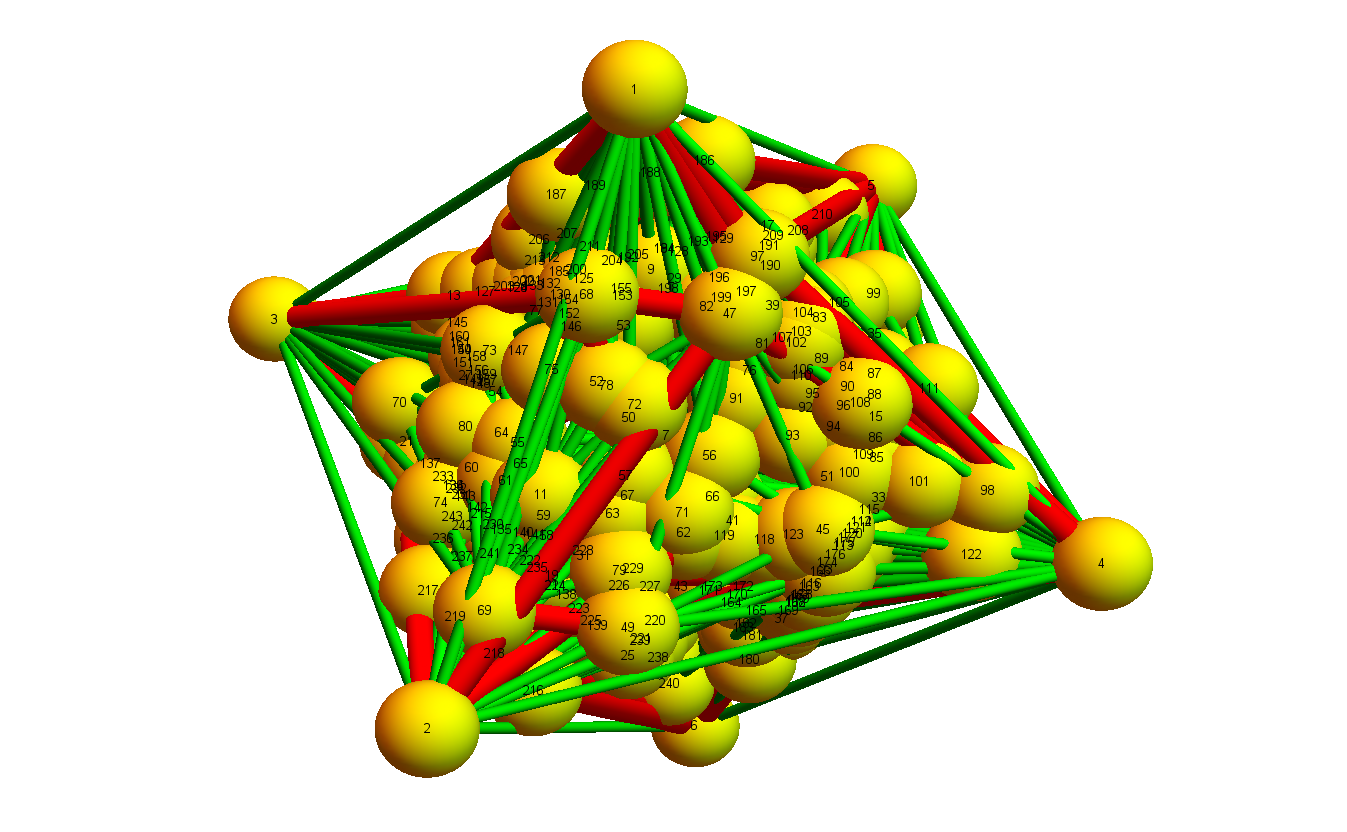
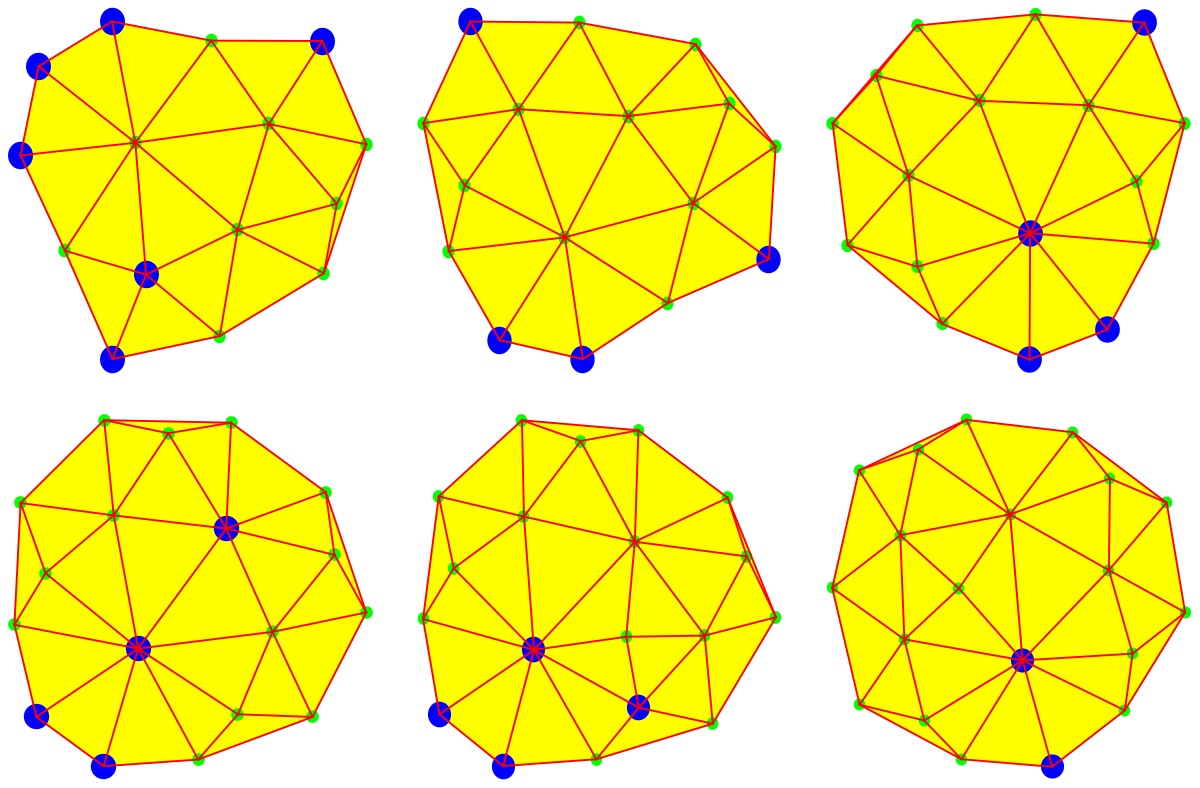
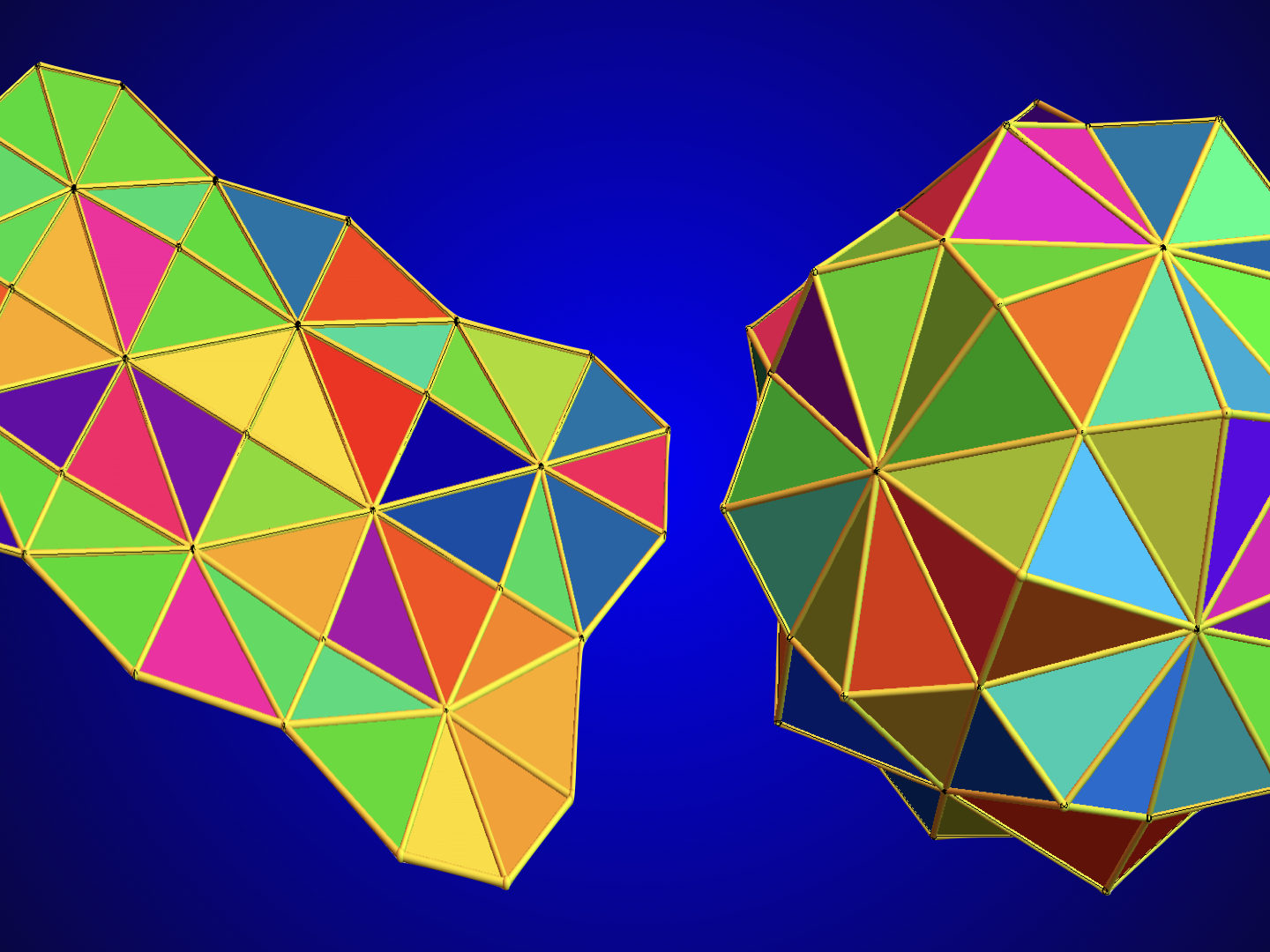
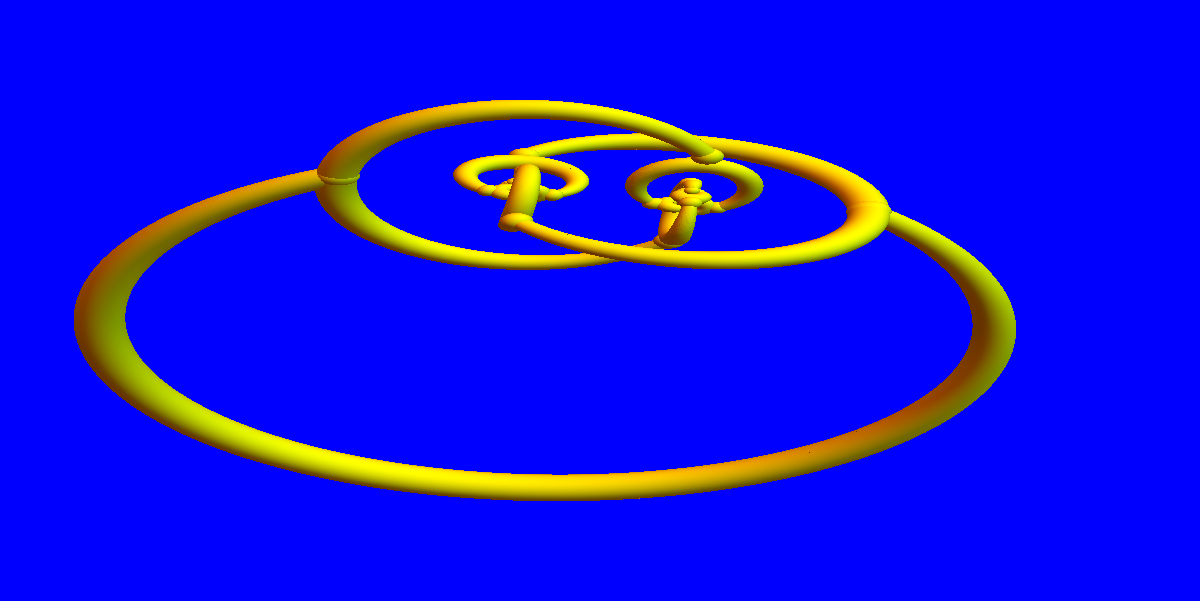
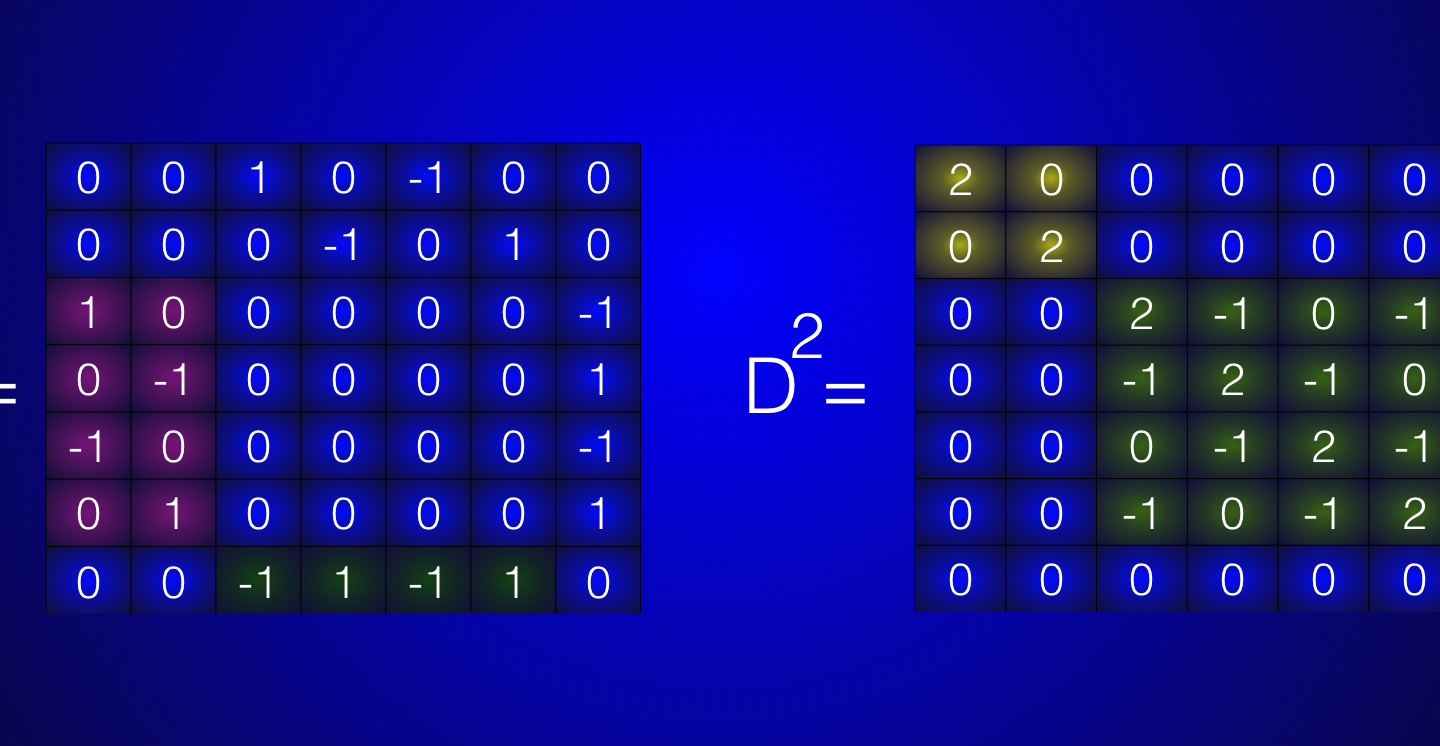
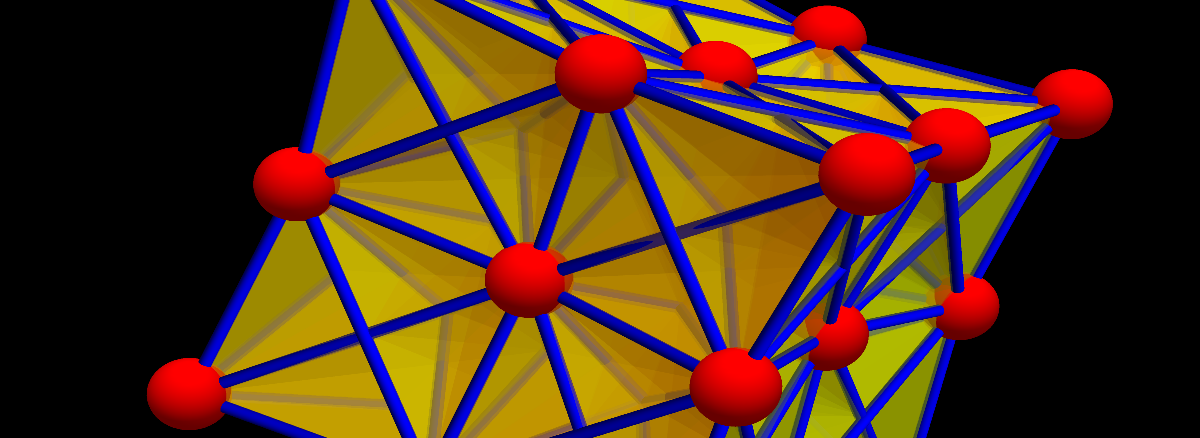
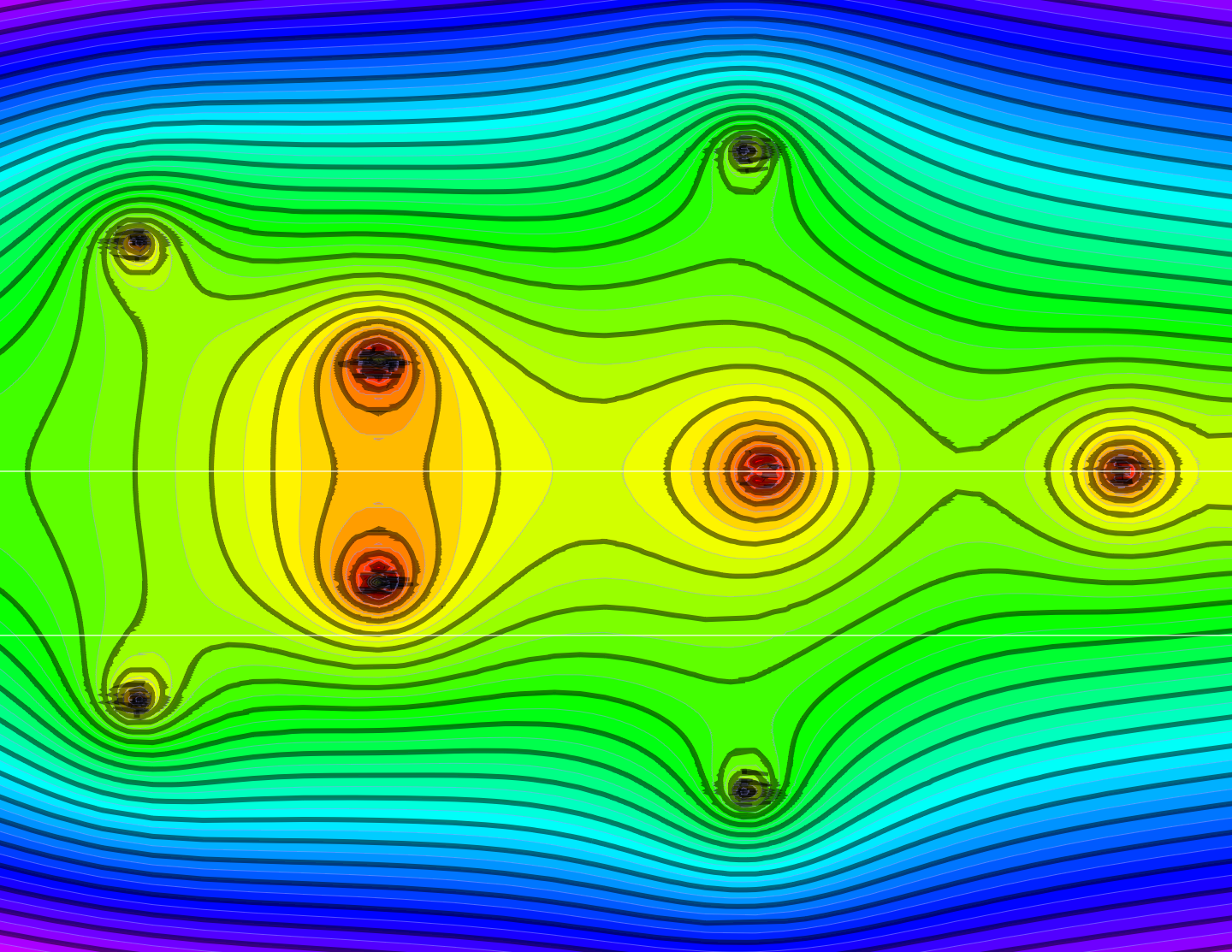
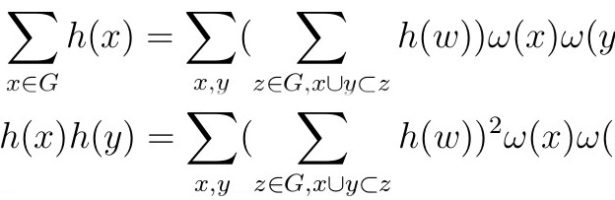Discrete Billiards
One can for discrete billiards ask questions which are classical in the continuum. One of them is Guillemin’s conjugacy problem, which is an inverse problem. It is problem 6 in my personal favorite list of open problems in Hamiltonian dynamics from 25 years ago. This is a problem which in …